From the verdant leaves on trees to the vibrant green color in some of your favorite foods, the presence of chlorophyll is a common denominator. Today, we delve into one such chlorophyll derivative known as E140, a food coloring agent that brings more than just a pop of color to the table.
Key Takeaways
| 📌 E140 is generally considered halal as long as the extraction process is not contaminated with Haram substances. |
| 📌 E140 Chlorophylls are natural green pigments derived from plants and play a vital role in photosynthesis. |
| 📌 They are generally considered safe, but excessive consumption may lead to mild digestive discomfort or green-colored urine/feces. |
What Is E140 Chlorophylls?
E140 Chlorophylls are natural green pigments derived from plants. They play a critical role in the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert carbon dioxide into oxygen and glucose using sunlight.
In the realm of food, E140 is employed as a coloring agent to provide a visually appealing green hue to various products. The use of natural coloring agents like E140 is a testament to the food industry’s initiative towards utilizing more natural and less synthetic additives.
But what makes E140 unique at the molecular level?
Chemical Structure
The chemical structure of E140 is fascinating and quite complex. At its core, it consists of a porphyrin ring coordinated with a central magnesium ion. This structure is similar to that of heme, but with magnesium replacing iron. The presence of long phytol tails makes chlorophylls lipophilic, allowing them to integrate into cellular membranes easily.
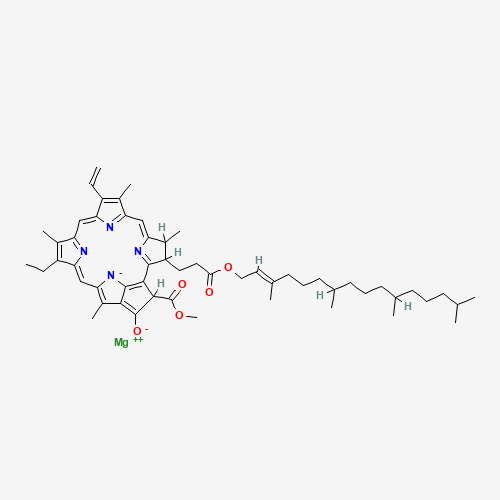
Moreover, the variation in side groups and the coordination of the central metal ion give rise to different types of chlorophyll molecules, each with its unique set of properties and potential applications. The molecular dance that unfolds within E140 is emblematic of nature’s ability to conjure up compounds of significant utility and beauty.
Curious about where E140 comes from?
What Is E140 Made From?
E140 is primarily extracted from green plants such as alfalfa or nettles. The extraction process involves removing the chlorophyll from the plant material using solvents, followed by further purification to obtain the desired color intensity and purity.
The source material and the extraction process play a pivotal role in determining the quality and safety of the E140 chlorophylls produced. The more natural the source and the less chemical intervention involved in the extraction, the safer and more desirable the E140 pigment.
But, is there a flip side?
Possible Side Effects
While E140 is derived from natural sources, like any other substance, it may pose some side effects, especially when consumed in excessive amounts. Some individuals might experience digestive discomfort, loose stools, or green-colored urine or feces.
However, these side effects are generally mild and tend to resolve on their own. It’s a gentle reminder that even natural substances require a balanced approach.
How about the legal standpoint?
Regulations and Guidelines
The use of E140 is governed by food safety regulations which vary from region to region. In the European Union, for example, E140 is approved for use in certain food and beverage categories under the E number system. Similarly, other regions have their own set of guidelines governing the use, dosage, and labeling of E140.
This brings us to the next point, how much is too much?
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of E140 largely depends on the particular food or beverage product it’s being used in. The acceptable daily intake (ADI) is determined by food safety authorities based on various factors including the type of food, the population demographic, and existing scientific data on E140’s safety profile.
Unfortenately, the ADI level for Chlorophylls has not been established by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) or the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) since chlorophylls are not of safety concern as regards their current use as food additives
Now, a common query arises, is E140 permissible in a Halal diet?
Is E140 Halal or Haram?
The Halal status of E140 is subject to the source from which it is derived and the process of extraction. If E140 is extracted from Halal-certified plants and the extraction process does not involve any Haram (forbidden) substances, it is deemed Halal. It’s imperative to check the certification and the labeling of the product to ascertain its Halal status.
Find out more:
Is E133 Halal or Haram?
Is E1404 Halal or Haram?
Let’s tie up the loose ends.
Final Words
E140 Chlorophylls offer a natural alternative to synthetic food colorings. Their use, governed by stringent regulations, and their origin from the heart of nature, places them in a favorable light among both manufacturers and consumers.
As we explore the boundaries of natural food additives, E140 stands as a testament to the symbiotic relationship between nature and our food systems.
Allahu A’lam (Allah Knows Best)
FAQ
What is the source of E140?
The source of E140 or Chlorophyll is a natural green color, which is present in all plants and algae. Chlorophyll is commercially extracted from various sources, including nettles, grass, alfalfa, and other plant materials.
Is E140 safe for consumption?
Chlorophylls are generally considered safe and do not have any known side effects when consumed in normal amounts
What are some common food products that contain E140?
Various beverages, candies, and baked goods may contain E140 for coloration.
What is the CAS number of E140?
The CAS number for chlorophyll is 1406-65-1.
Is E140 banned in any country?
E140 or Chlorophylls are not banned in any country. However, regulations vary, and it’s essential to check local food safety guidelines for E140’s status in your region.
- Is Pop Tarts Halal? What You Need to Know - February 18, 2024
- Are Graham Crackers Halal in Islam? - January 19, 2024
- Is Keebler Wheatables Halal? - January 18, 2024





